
What is a Cutting Plotter Machine?
Do you want know about, What is a cutting plotter machine? in this blog we will tell all things about cutting plotter machine. A cutting plotter machine, also known as a vinyl cutter or cutting plotter, is a computer-controlled machine that precisely cuts patterns, designs, and lettering out of thin materials like vinyl, cardstock, and specialty media. It works by using a sharp blade or stylus to cut along vector paths created through design software.
These machines are incredibly versatile tools used for a wide range of projects and applications from vehicle graphics and signs to apparel decoration, window tinting, and even hobbies like scrapbooking and card making. The precise cutting capabilities of a plotter allow for intricate designs that would be impossible or incredibly tedious to cut by hand.
Types of Vinyl Cutting Plotters
There are several different types of plotters:

Vinyl Cutting Plotters
These are computer-controlled machines that use a sharp blade or stylus to cut vector shapes and designs out of thin materials like adhesive vinyl, transfer vinyls, cardstock, etc. They are extremely popular for sign making, vehicle graphics, apparel decoration, and crafts.

Drum Plotters
Flatbed plotters have a flat surface that the media lays on top of. The pen or cutting tool moves on a gantry system over the stationary media. Many modern vinyl cutters have a flatbed design.
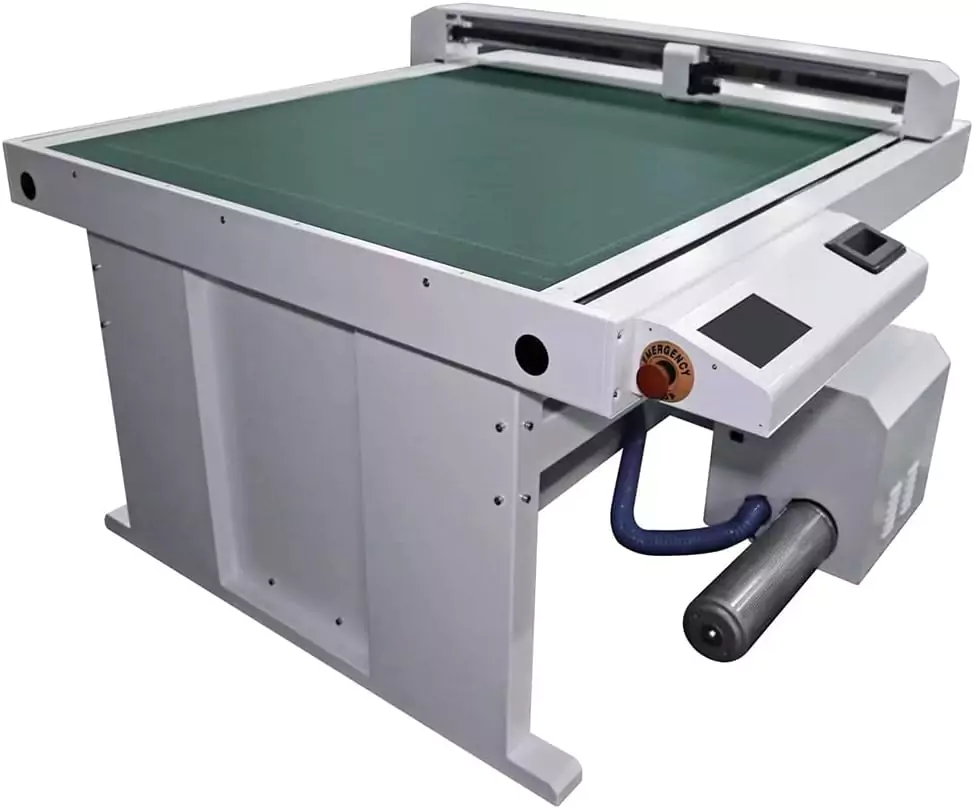

Flatbed Plotters
Flatbed plotters have a flat surface that the media lays on top of. The pen or cutting tool moves on a gantry system over the stationary media to draw or cut the design. Many modern cutting plotters for vinyl/materials are flatbed style. Some integrate sensors for print/cut contour cutting.
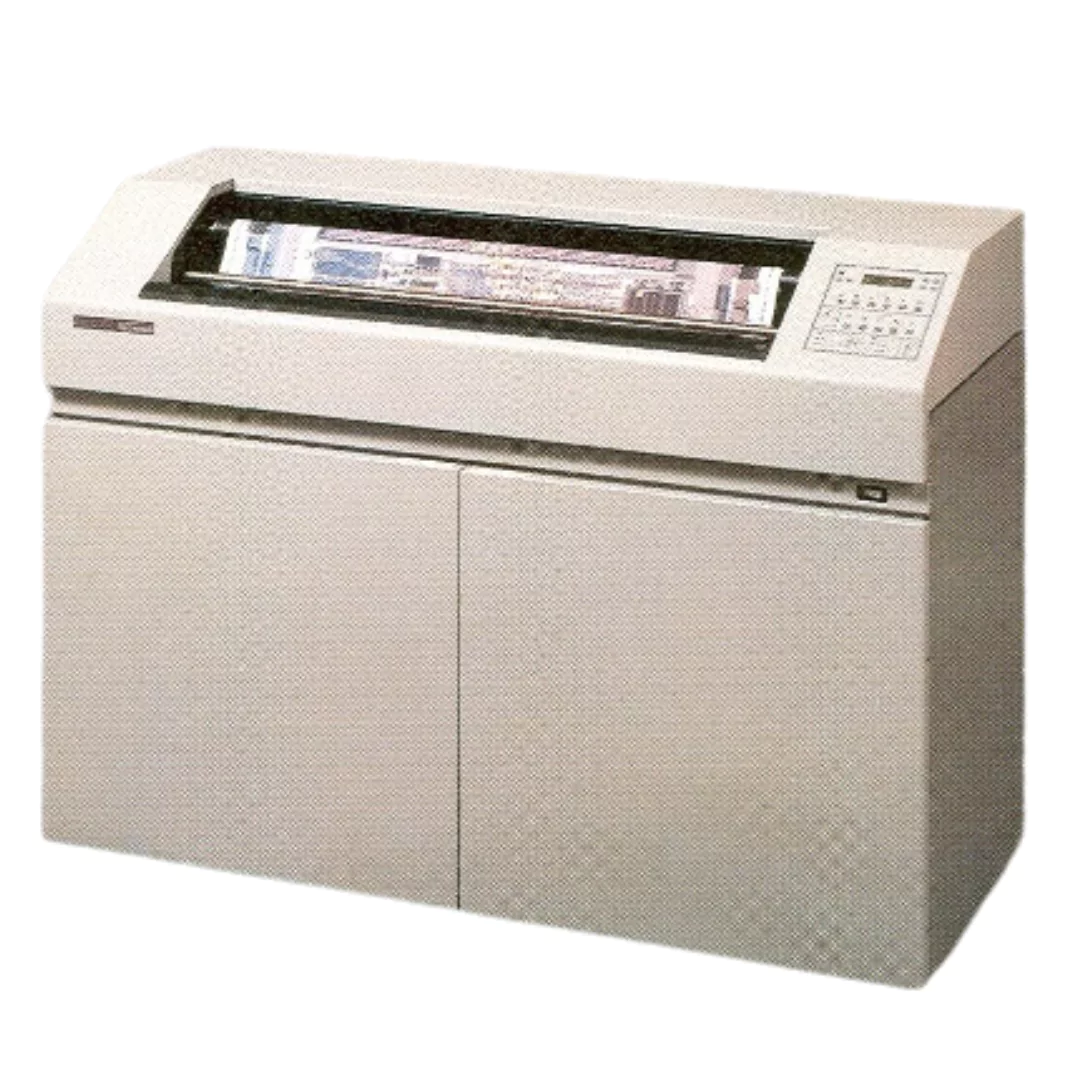

Electrostatic Plotters
These specialized plotters use electrostatic technology to create the image, drawing with a charged toner onto a dielectric surface. Electrostatic plotters can plot very high resolutions but are limited in line width and media types. They were mainly used for engineering drawings.
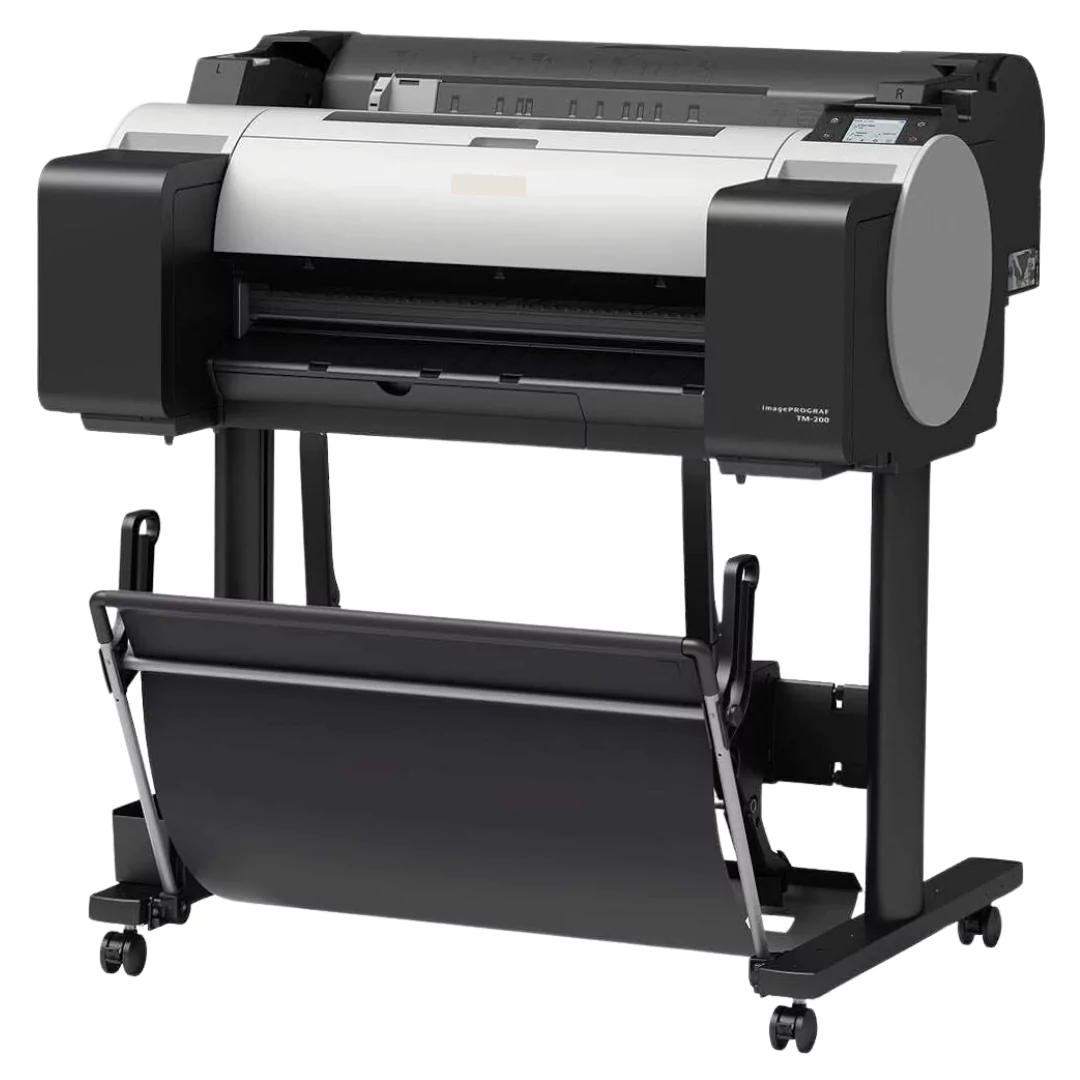

Inkjet Plotters
Inkjet plotters are large-format printers that use inkjet technology to print high-quality drawings, renderings, and graphics onto media like paper, vinyl, or canvas. They can produce multi-color output and are a more modern plotter style versus the older pen plotters.
Pen Plotters
Traditional pen plotters use a pen, pencil, or other drawing tool on a hanging-head to draw vector images onto paper or film media. They were once common for drafting, mapping, and design work before being largely replaced by printers/plotters using newer technologies.
Of these, the most commonly used today are flatbed cutting plotters for cutting vinyl, inkjet wide-format printers for printing/plotting, and specialized plotting machines in industrial design workflows. The drum and electrostatic pen plotting methods have faded as analog technologies.
What is a Cutting Plotter Used For?
Cutting plotters have a vast array of uses across many industries and applications including:

- Sign Making and Vehicle Graphics

- Apparel/Merchandise Decoration

- Window Tinting and Architectural Detailing

- Craft/Hobby Projects

- Packaging Prototypes and Samples

- Customized Stickers and Decals

- Flock, Flex, and Speciality Media Applications
These versatile machines allow cutting incredibly intricate shapes, patterns, and typography from thin, flexible materials with amazing accuracy. Their digital cutting capabilities open up new creative and commercial opportunities.
Can a Cutting Plotter Print?
No, cutting plotters do not have any printing capabilities. They are designed solely for cutting vector shapes out of loaded materials using a blade or stylus. If graphics need color or raster images added, that would require a separate vinyl printer or large format printer to print the design first before cutting it out on the plotter.
Some newer generation printer/cutter combos do integrate print and cut functionality into a single unit, but they perform each task separately with dedicated print heads and a cutting tool. But traditional standalone cutting plotters cannot print on their own.
What Are 5 Functions of a Plotter?
While plotting/cutting different materials is their primary function, cutting plotters offer several key capabilities:
- Precision Cutting – Plotters use stepper motors and servo controls to accurately follow vector paths and cut intricate shapes, patterns, and text.
- Material Versatility – They can cut adhesive vinyl, transfer vinyls, speciality media, cardstock, thin plastics, and more.
- Contour Cutting – Optical sensors allow plotters to contour cut printed designs by reading registration marks.
- Creasing/Scoring – Some models have tools for scoring materials like paperboard for folding applications.
- Plot Cutting/Plotting – Not just for adhesive vinyl, plotters can plot and cut paths on other thin, flexible media.
Are Plotters Still Used?
Absolutely, cutting plotters continue to have many important applications and uses in various industries in the modern era. While printing technology has expanded with large format eco-solvent and UV printers, plotters provide precise cutting abilities that are invaluable.
Traditional plotters optimized for cutting adhesive vinyl for sign making and vehicle graphics continue to be workhorses. But newer cutting plotter models have evolved with expanded material capacities, improved accuracy, and the ability to cut speciality media, opening up new creative and manufacturing uses.
Far from being outdated, cutting plotters remain essential tools for custom signage, apparel decoration, product prototyping, packaging design, and more. Their combination of accuracy, versatility, and digital integration ensures plotters will have an important role for years to come.
Can a Vinyl Cutter Cut Stickers?
Yes, one of the most common uses for vinyl cutters is producing custom stickers and decals. Both adhesive backed vinyl and printable vinyl or paper materials can be used to cut detailed stickers in any design. Sign shops, craft suppliers, and e-commerce sticker businesses all utilize vinyl cutters for on-demand sticker production.
The precision and versatility of vinyl plotters allow them to cut highly intricate sticker designs including fine details, text, and contour cut printed designs with an optical sensor. Whether its basic shape stickers, die cut vinyl decals, or intricately detailed designs, vinyl cutters are ideal sticker making tools.
What Are the Advantages of Using a Vinyl Cutter?
Using a vinyl cutter for cutting adhesive vinyl, transfer materials, speciality media, and other thin flexible substrates offers many advantages:
Precision – Computer numerical control allows for incredibly accurate and intricate cuts not possible by hand.
Speed – Automated cutting is much faster than manual cutting, especially for complex designs.
Versatility – Plotters can cut a wide range of flexible materials in different thicknesses and patterns.
Consistency – Every cutline is perfectly consistent and repeatable. No variation from human error.
Digital Integration – Vector files from design software can be sent directly to the plotter for cutting.
What Do You Need for a Vinyl Cutter?
To setup and use a vinyl cutting plotter, you’ll need the following:
Vinyl Cutter – The cutting plotter machine itself, options range from hobbyist desktop cutters to professional sign shop models.
Design Software – A program to create the vector cut paths/artwork files like Adobe Illustrator, Inkscape, or integrated software.
Cut Files – Artwork files in a compatible vector format like .ai, .pdf, .svg, etc. to send to the cutter.
Vinyl/Media – Adhesive backed vinyl, heat transfer vinyl, speciality media, etc. to be loaded for cutting. Match media to the cutter’s force and downforce capabilities.
Cutting Tools – The cutter blade/stylus/tool installed on the machine and appropriate for the media thickness.
Accessories – Optional vinyl baskets/flanges, cutting mats, weeding tools depending on the project.
With the right vinyl cutter, design software, cut files, media and tools, you can start producing custom vinyl graphics, signs, apparel decoration, stickers, and more with digital precision.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages of Using a Vinyl Cutting Plotter?
Like any tool, vinyl cutting plotters have their own unique pros and cons to consider:
Advantages:
Precision – Vector cutting produces incredibly accurate, intricate designs and text.
Versatility – Can cut adhesive vinyl, heat transfer material, speciality media, etc.
Consistency – Automated precision cutting is perfectly repeatable with no variation.
Digital Integration – Cut directly from vector artwork created in design programs.
Automation – Efficient automated cutting process once designs are loaded.
Disadvantages:
Material Limitations – Can only cut relatively thin, flexible media up to the cutter’s max force. No rigid materials.
Vinyl Expenses – Ongoing costs of vinyl, transfer media, blades, etc. can add up.
Learning Curve – Takes some training to learn operation and compatible design programs.
Limited Colors – Cannot print color, needs separate printing for raster graphics.
Single Purpose – Cutting is its sole function, not an all-in-one solution.
Overall, the advantages of precision cutting, versatility, and fast automated operation make vinyl cutting plotters extremely valuable tools. Limitations like material compatibility and upfront learning curve are outweighed by the capabilities for professional vinyl work and custom projects.
Conclusion
Cutting plotters, commonly referred to as vinyl cutters, are incredibly versatile computer-controlled machines capable of precisely cutting intricate designs out of thin flexible materials like adhesive vinyl, transfer media, specialty films, and more.
While the principle of a sharp blade or stylus following vector paths may seem simple, these machines open up a world of creative and commercial opportunities through their digital automation, material versatility, and cutting accuracy.
From basic vinyl signs and graphics to custom apparel decoration, packaging prototypes, and specialty applications, cutting plotters have carved out an indispensable niche across many industries. And with their expanded media capabilities and integration with design software, they will continue to be valuable tools for years to come.
So whether you’re a sign professional, crafter, or exploring new business ideas, investing in the right vinyl cutting plotter can be a game-changer. With the proper setup, materials, and design skills, this digital cutting technology allows you to unleash your creativity while producing incredible custom results.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, vinyl cutting plotters cannot print. They are designed solely for cutting patterns out of loaded materials like adhesive vinyl and speciality media. Printing requires a separate vinyl printer or large format printer.
Yes, all professional vinyl cutters require connection to a computer to receive the digital cut files and control the cutting. Entry-level hobbyist cutters may have onboard editing and wireless connectivity options.
For glass window graphics like storefront lettering or decals, use outdoor rated vinyl intended for that application like Oracal 651 or Avery 900 Super Cast vinyl.
Most quality cast vinyl from 3M, Avery, etc. is rated for 5-7 years of UV and weather exposure when applied properly. Lower cost calendered vinyl may only last 3-5 years outdoors.
Match the blade type and offset to your specific vinyl cutter model and the thickness of material being cut. For example, a 60° blade may be used for thinner vinyls while a 45° blade can cut thicker media.
